Simulation of a flock of birds
The goal of this work is to create an animation of a flock of birds that behaves according to Reynolds' boids model. Additional rules are considered to grant obstacle avoidance to the flock and boundary constraints to avoid the spreading of the flock out of the fi eld.
Modelling and animating the birds
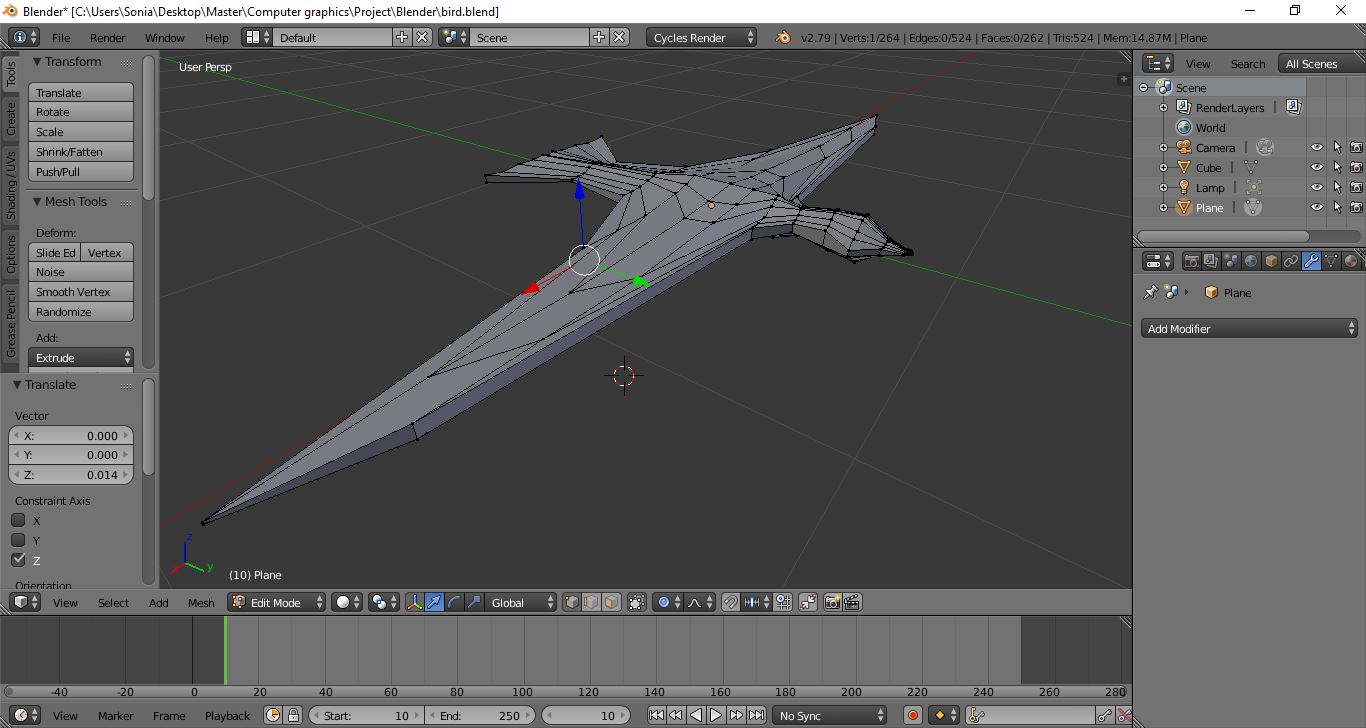
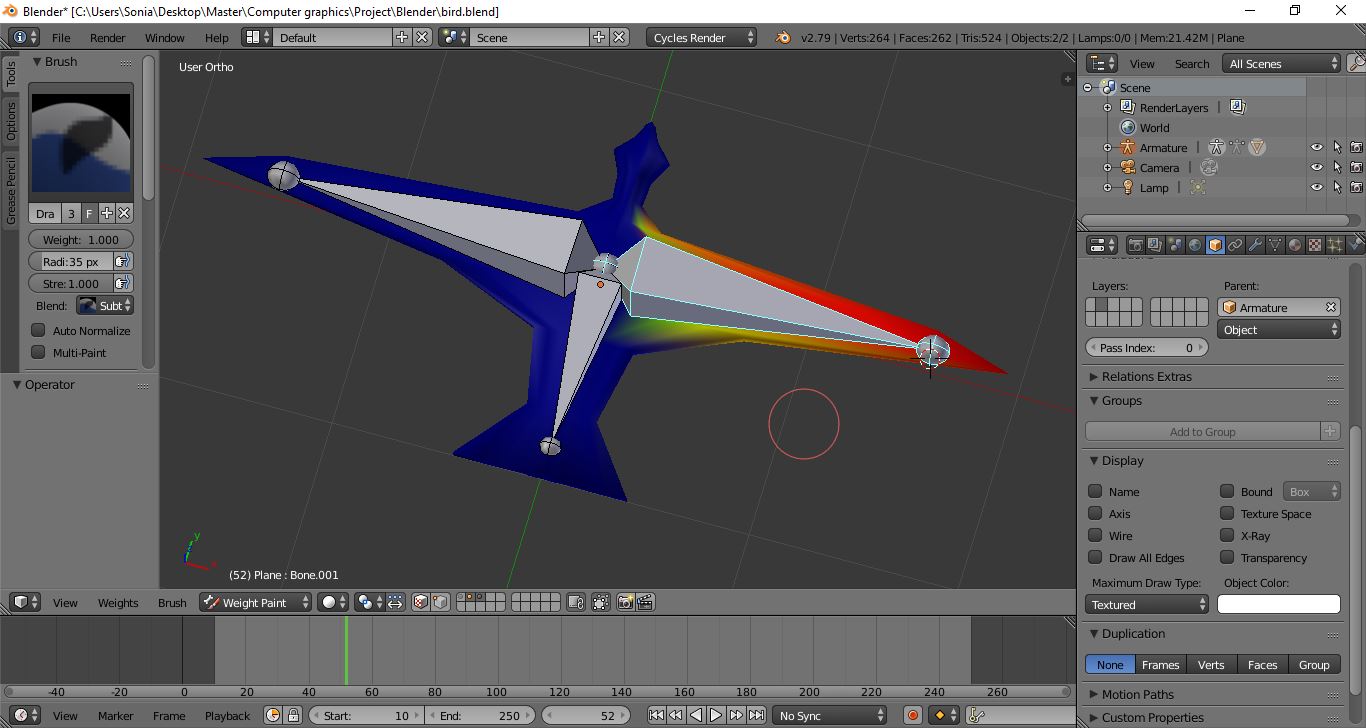
In order to create the 3D model and the flying animation of the birds, the open source software Blender was used. A simple armature was added to the model, with a main bone in the body and two bones for the right and left wings. The model was imported into Unity to be used as the prefab for the autonomous agents. Only the flying animation was designed, which involved that the birds will not stop at the ground at any moment. This additional state could be implemented as future work.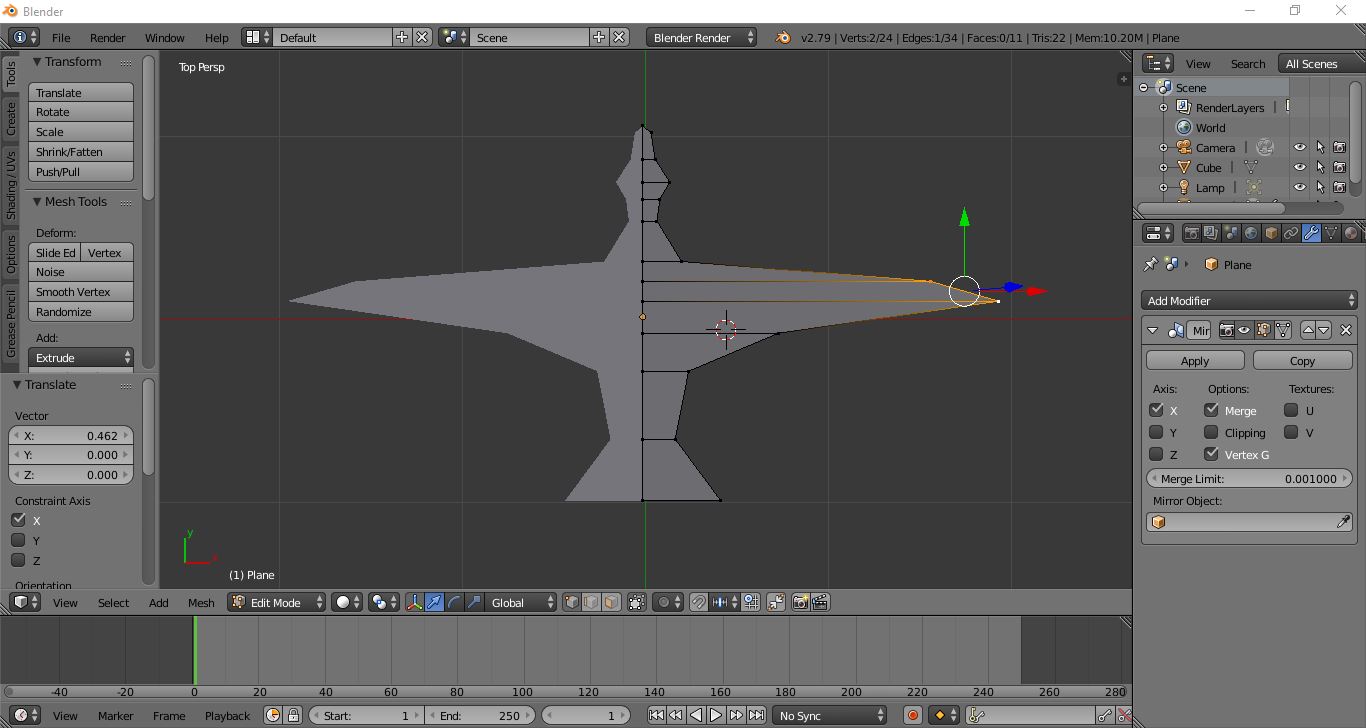
Implementing boids algorithm in 2D
The implementation of the boids simulation algorithm started with a simplifi ed approach in 2D. The main reason for this was the ease to visualize and assure a correct behavior of the boids. A simple scene was created in Unity, with a flat plane as the floor and the boids moving exclusively in a plane parallel to it. The boids are instantiated in a uniform distribution around the fi eld and they always remain inside the boundary limits of the fi eld. In order to ful fill this requirement, a new component is added to the boids' velocity, forcing a change of direction towards the center of the fi eld when they pass the boundaries.
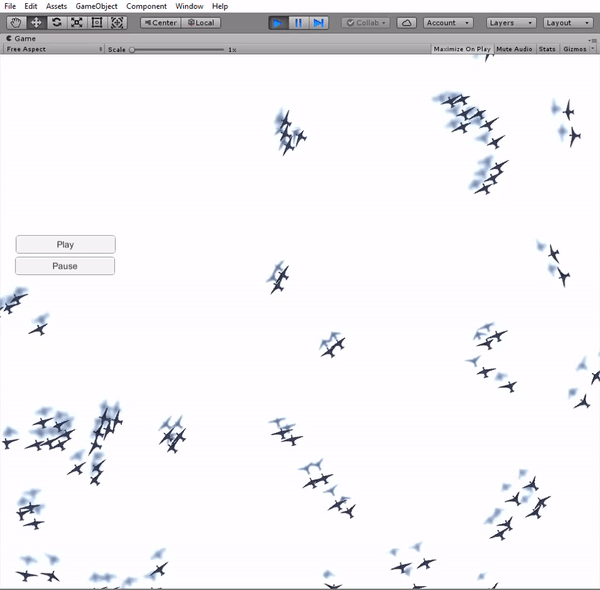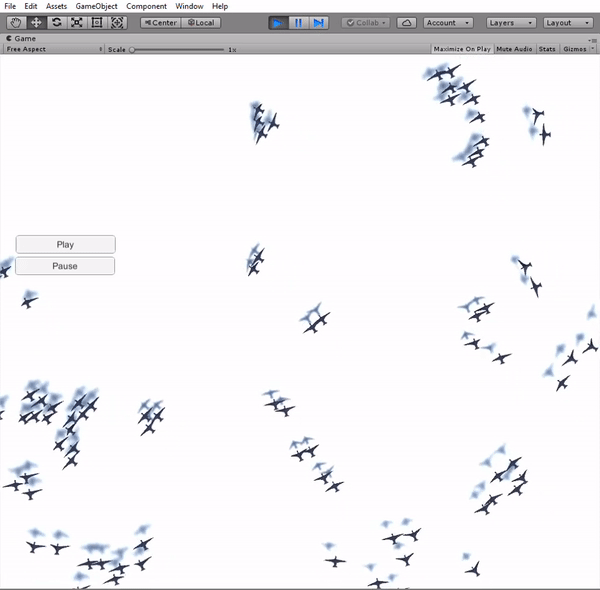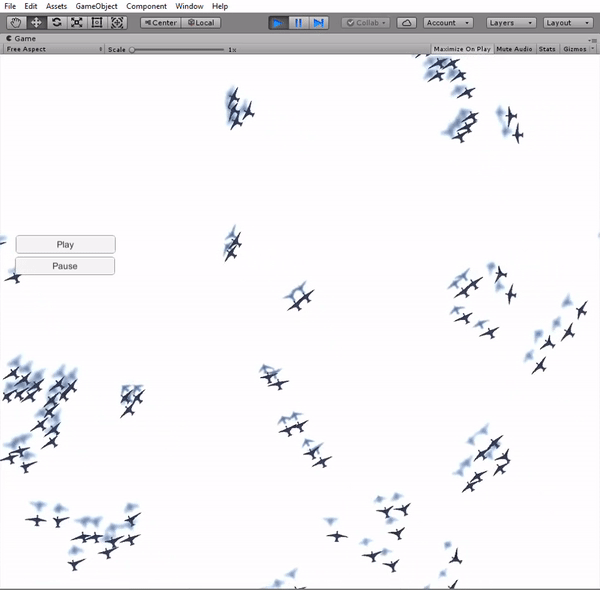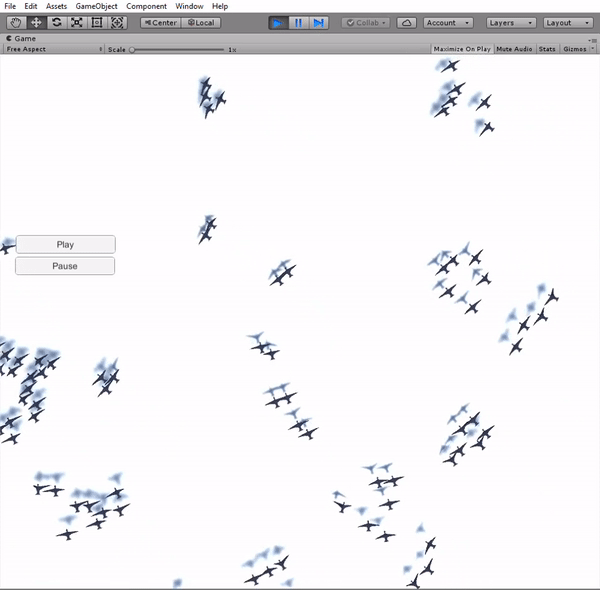
Simulation in 3D
So far, the implementation had been constrained to 2D. That means that the birds could only fly horizontally and all of them at the same height. The next step in the development process was to add a new degree of freedom by allowing the birds to fly freely in the three-dimensional space.
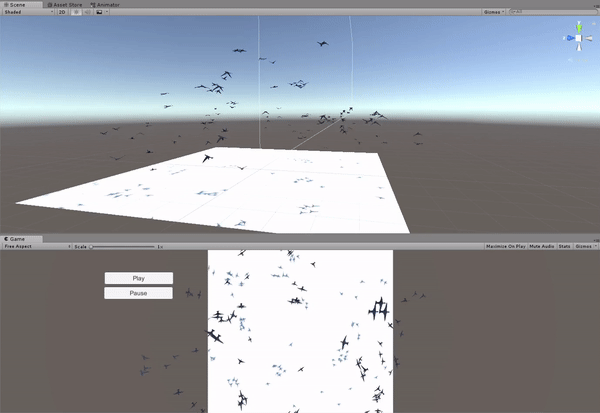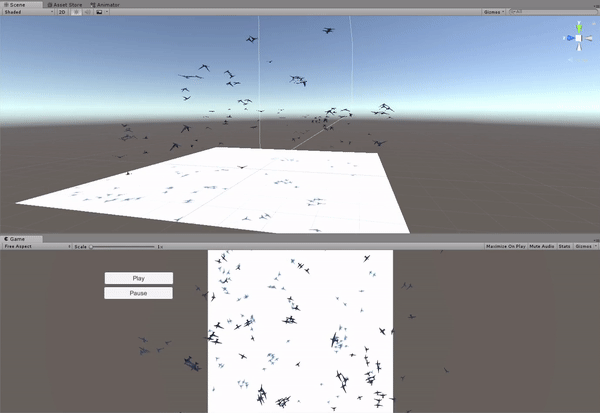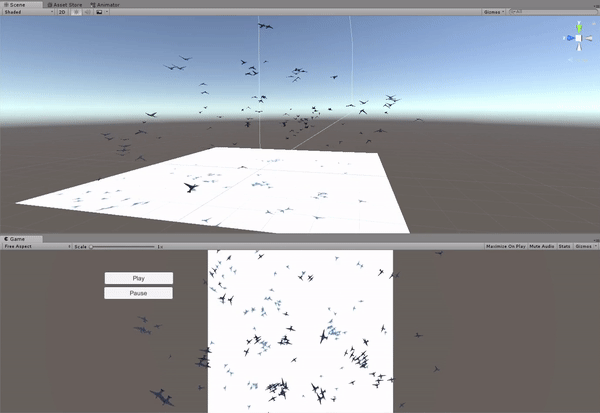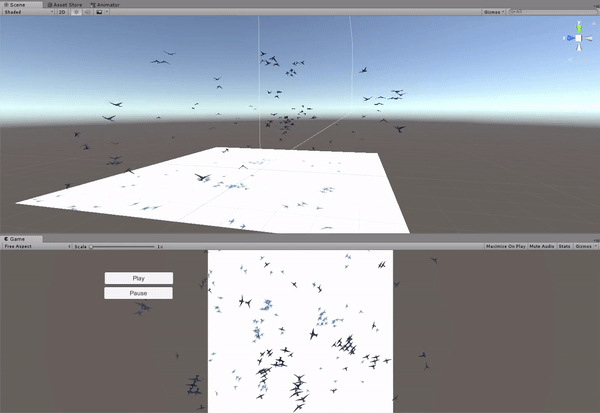
Generating the terrain in Unity
To add an extra level of realism to the scene, a new terrain was created replacing the previous flat ground. This forced the implementation of an additional interaction between the boids and the environment in order to avoid collisions. The landscape, formed by an irregular ground and high mountains, was modelled using Unity's Terrain Engine.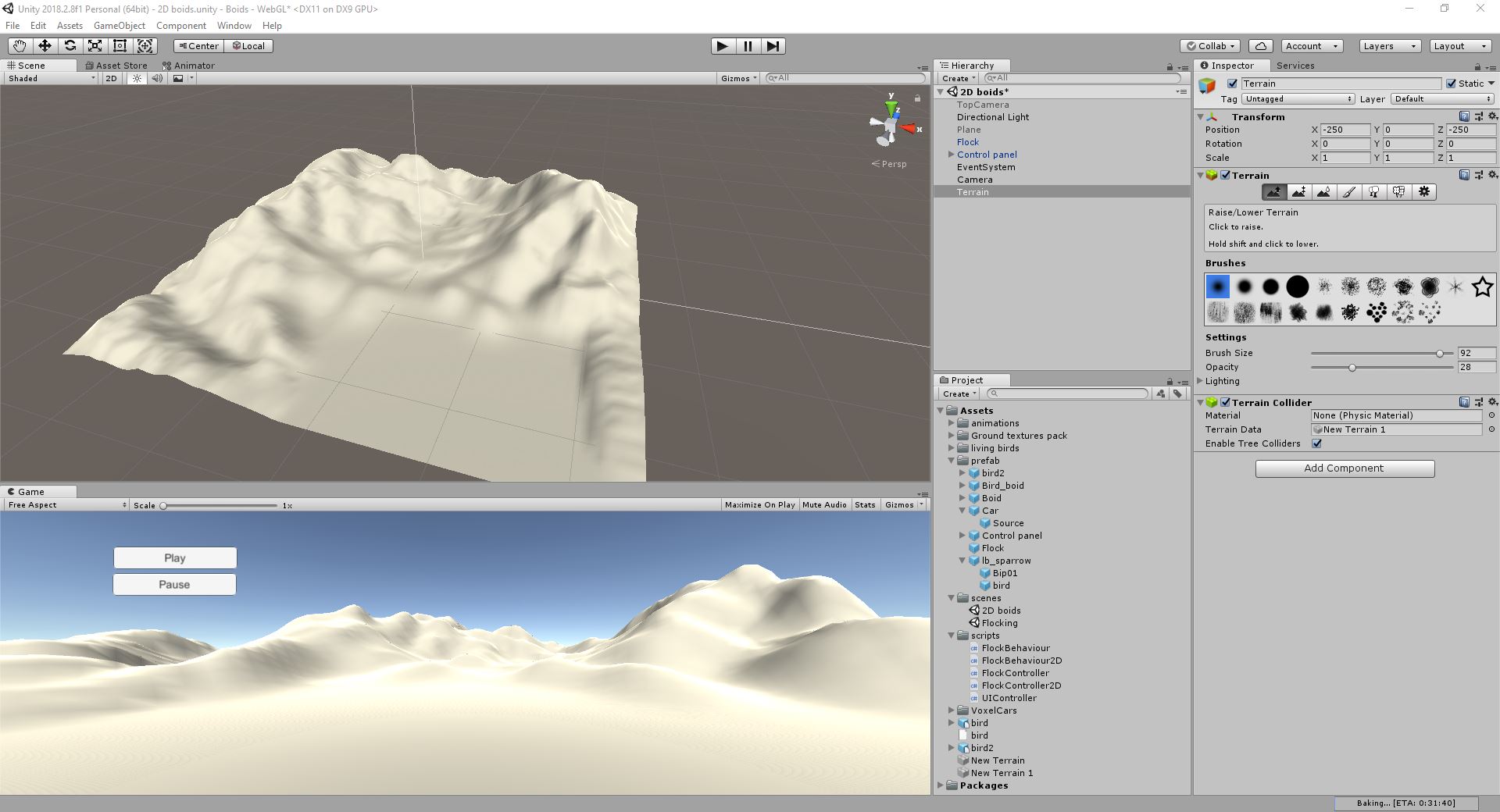
Avoiding obstacles
The boids control if there are any near obstacles in their movement direction. If an obstacle is detected, the boids need to change their direction to avoid it before colliding. A new behavioral component is added to the velocity of the boids (besides the cohesion, separation, etc.). This new component is equal to the reflection of the boid's current direction (its forward axis) from the surface of the hit obstacle. Before implementing the obstacle avoidance, the birds fly through the terrain since they are configured to not have colliders.
Before implementing the obstacle avoidance, the birds fly through the terrain since they are configured to not have colliders.
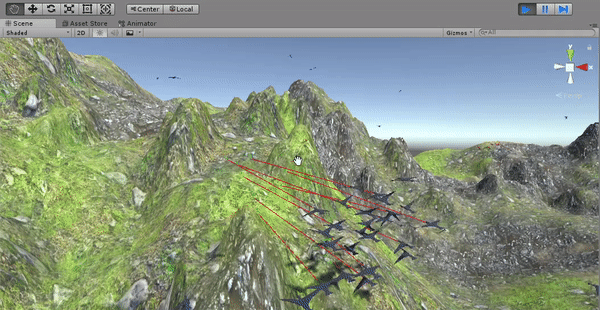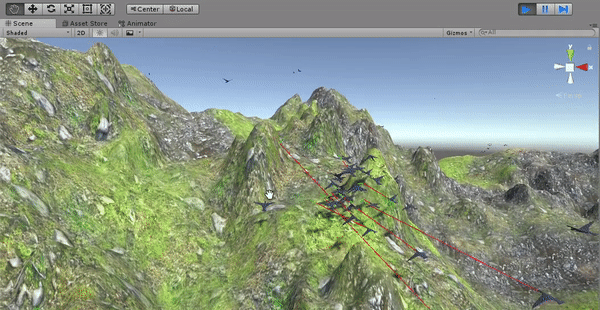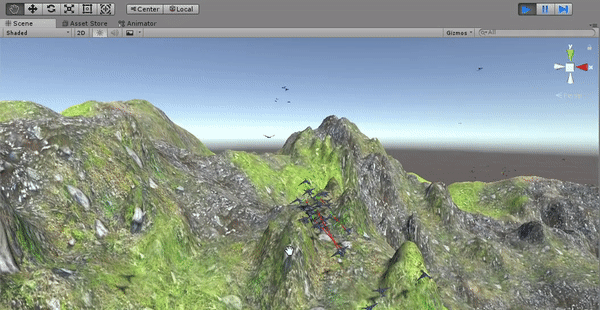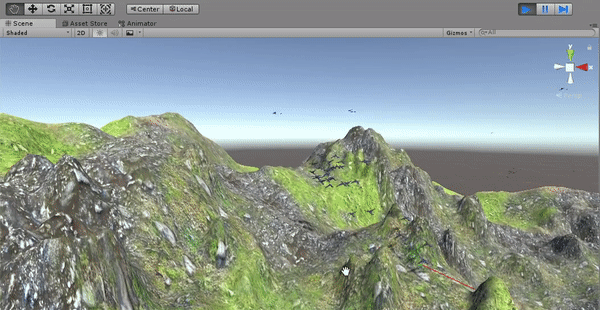 Collision is detected by raycasting and the velocity is modified in order to dodge the obstacles.
Collision is detected by raycasting and the velocity is modified in order to dodge the obstacles.
Real-time parameter tuning
In order to be able to manipulate the behavior parameters in real time, a control panel was added to the application as a GUI element. The options include Play/Pause, number of birds, neighborhood distance, separation distance and set default parameters. The values are selected via sliders and a callback function is in charge of updating the parameters in the simulation in real time.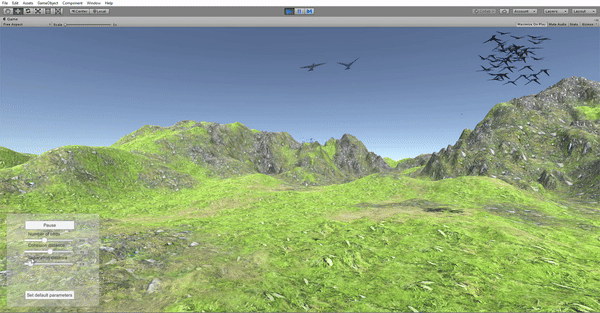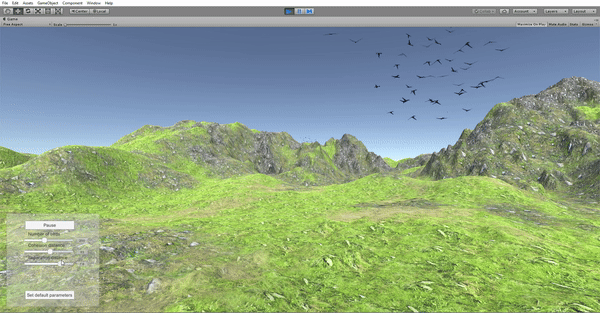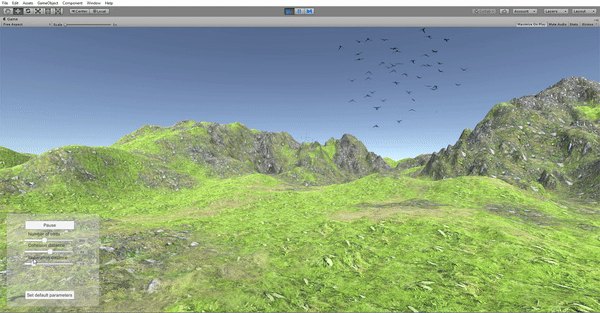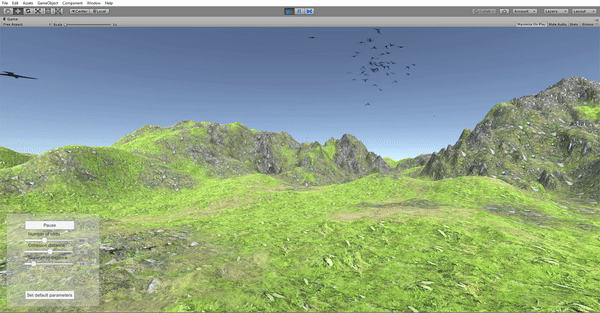 The separation distance is modified in real time and the video shows how that parameter affects the flock.
The separation distance is modified in real time and the video shows how that parameter affects the flock.